Plastic Injection Moulding enables fast, scalable, and cost-efficient mass production of high-quality plastic parts with precision and repeatability.
What Exactly Is Plastic Injection Moulding and Why Does It Matter?
Plastic injection moulding is the dominant manufacturing standard for creating plastic parts by injecting molten material into a metal mould. It stands out as the most efficient method for fabricating high-volume components with identical specifications.

Is Mass Production Feasible?
- Yes, it handles millions of cycles.
- The process ensures identical output every time.
- You gain economies of scale immediately.
Here is the deal: reliable mass production starts with this technology.
What About Material Versatility?
- You can choose from thousands of resin types.
- Options range from rigid ABS to flexible TPE.
- Additives can improve strength or heat resistance.
You might be wondering: does this limit your design creativity? Not at all.
Key Takeaway
Plastic injection moulding is the backbone of modern manufacturing, allowing for the rapid creation of complex, durable, and identical plastic parts at scale.
| Feature | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Core Function | Injecting molten plastic into a metal mould | |
| Primary Use | High-volume mass production | |
| Material Range | Extensive (Thermoplastics, Elastomers) |
The versatility of this process makes it indispensable for sectors ranging from consumer goods to aerospace.
How Does the Plastic Injection Moulding Process Work Step by Step?
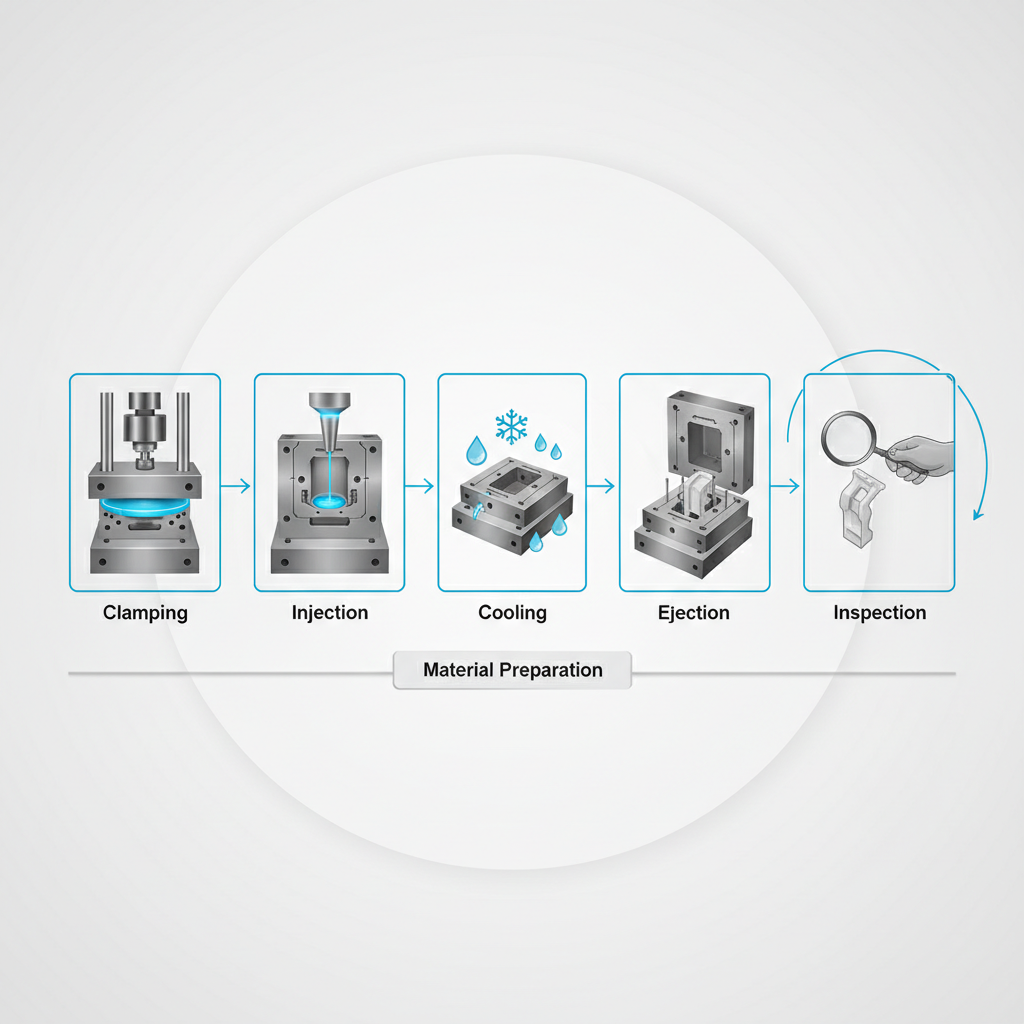
The process operates on a continuous cycle where a machine melts plastic, shoots it into a form, and ejects a finished part. This plastic injection moulding cycle repeats rapidly, ensuring high output in a short timeframe.
What Are the Machine Components?
- The Hopper holds the raw plastic granules.
- The Barrel heats and melts the material.
- The Reciprocating Screw moves the plastic forward.
But here is the kicker: the machine precision dictates the part quality.
How Fast Is the Cycle?
- Simple parts take seconds to mould.
- Complex geometries might take a minute.
- Cooling time usually drives the speed.
Ready for the good part? Faster cycles mean lower unit costs for you.
Key Takeaway
The cycle comprises five distinct stages—clamping, injection, cooling, ejection, and inspection—that work in harmony to produce parts efficiently.
| Step | Action | Time Factor | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Clamping | Secures mould halves | Instant | |
| 2. Injection | Fills cavity | Fast (Seconds) | |
| 3. Cooling | Sets plastic | Variable (Longest) |
Understanding this cycle helps you optimize design for faster production runs.
Why Is Clamping Vital in Plastic Injection Moulding Operations?
Clamping is the first critical step where the two halves of the mould tool are held tightly together by a powerful hydraulic or toggle unit. Without this immense pressure, the force of the incoming plastic would push the mould open, ruining the part.

Why Is Pressure So Important?
- It counteracts the force of injection.
- It keeps the parting line sealed tight.
- Tonnage requirements depend on part size.
What is the real story? Undersized clamps lead to immediate product failure.
How Does It Prevent Defects?
- A tight seal prevents “flash” (excess plastic).
- It ensures dimensional accuracy.
- It protects the mould from damage.
Here is a secret: Flash is one of the most common and costly defects to fix.
Key Takeaway
The clamping unit must provide sufficient force to keep the mould closed against the high pressure of the injected plastic, ensuring a clean, defect-free product.
| Component | Function | Criticality | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stationary Platen | Holds the fixed mould half | High | |
| Moving Platen | Closes the mould | High | |
| Tie Bars | Support clamping force | High |
Proper clamping tonnage calculation is a fundamental aspect of setting up a successful production run.
How Does Injection Occur in Plastic Injection Moulding Machinery?
During this phase, raw pellets are melted and forced into the mould cavity by a hydraulic ram or screw. In plastic injection moulding , this step defines the part’s shape and density.

How Is Plastic Melted?
- Heater bands warm the barrel.
- Friction from the screw generates heat.
- The result is a consistent molten flow.
It gets better: The temperature control is precise to within a few degrees.
What Is Injection Pressure?
- It is the force pushing the melt.
- High pressure fills complex details.
- It packs the material to prevent shrinkage.
Think about this: Without packing pressure, your part would have sink marks.
Key Takeaway
The injection stage transforms solid granules into a precise liquid form that fills the mould cavity completely, capturing every detail of your design.
| Parameter | Typical Range | Impact | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Melt Temp | 200°C – 300°C | Flow Rate | |
| Injection Pressure | 10,000 – 30,000 PSI | Part Density | |
| Fill Time | < 1 Second – 5 Seconds | Surface Finish |
Optimizing injection speed and pressure is the primary skill of a moulding technician.
Why Is Cooling Critical in Plastic Injection Moulding Cycles?
Cooling is the process where the molten plastic solidifies inside the mould to retain the desired shape. This step often consumes the majority of the cycle time and directly influences the final structural integrity of the part.

How Do Cooling Channels Work?
- Water flows through channels in the metal.
- They draw heat away from the hot plastic.
- Uniform cooling prevents warping.
You might be asking: can we skip this to save time? Absolutely not.
What Controls Material Shrinkage?
- Proper cooling sets the dimensions.
- Ejecting too hot causes deformation.
- Different plastics shrink at different rates.
Here is the bottom line: Cooling creates the stability your product needs.
Key Takeaway
Efficient cooling channels inside the mould are necessary to solidify the part quickly while maintaining dimensional accuracy and preventing warpage.
| Material | Cooling Speed | Shrinkage Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene | Medium | High | |
| ABS | Fast | Low | |
| Nylon | Slow | Medium |
The design of the cooling system is just as important as the design of the part itself.
How Are Parts Ejected in Plastic Injection Moulding Systems?
Once the part is solid, the mould opens, and the machine mechanically pushes the component out. In plastic injection moulding , this ejection must be forceful enough to remove the part but gentle enough to avoid damage.

What Are Ejector Pins?
- Steel pins that extend from the mould base.
- They push on the B-side of the part.
- They leave small, visible marks.
Here is a heads-up: You need to decide where these marks go during the design phase.
How Do Automated Systems Help?
- Robots can grab parts upon ejection.
- This prevents parts from falling and scratching.
- It speeds up the cycle reset.
Ready for the next step? Your part is now physically complete.
Key Takeaway
Ejection is the final mechanical movement of the cycle, requiring careful mould design to ensure parts release cleanly without sticking or bending.
| Ejection Method | Best For | Consideration | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pins | Standard parts | Leaves marks | |
| Stripper Plate | Round/Cup shapes | More expensive | |
| Air Blast | Lightweight parts | No physical marks |
Seamless ejection is the sign of a well-engineered mould tool.
What Is the Role of Inspection in Plastic Injection Moulding?
Inspection is the quality control phase where parts are checked for defects immediately after production. This step ensures that the machine settings are correct and that the output meets your rigorous specifications.

What Are Common Defects?
- Sink Marks: Depressions in thick areas.
- Flash: Excess plastic on edges.
- Short Shots: Incomplete filling.
What is the catch? Even one bad parameter can ruin a whole batch.
Why Is Trimming Necessary?
- Removes the “gate” (entry point).
- Cleans up any flash.
- Prepares the part for assembly.
Here is the truth: Automated inspection cameras are becoming standard for zero-defect goals.
Key Takeaway
Continuous inspection provides immediate feedback to the manufacturing team, allowing them to adjust parameters and maintain high quality standards.
| Defect Type | Cause | Solution | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Burn Marks | Trapped gas | Improve venting | |
| Flow Lines | Variable speed | Adjust injection speed | |
| Warping | Uneven cooling | Redesign cooling lines |
Quality assurance is the bridge between raw manufacturing and a market-ready product.
Which Industries Rely on Plastic Injection Moulding Solutions?
From intricate medical devices to rugged automotive components, plastic injection moulding serves almost every sector of the modern economy. Its ability to scale makes it the go-to choice for global industries.

How Does Automotive Benefit?
- Lightweight bumpers and dashboards.
- High durability for engine components.
- Cost reduction replacing metal.
You might be surprised: Your car interior is almost entirely injection moulded.
Why Is It Vital for Medical?
- Sterile, single-use manufacturing.
- Extreme precision for surgical tools.
- Biocompatible material options.
Here is the deal: Patient safety relies on this consistency.
Key Takeaway
The versatility of injection moulding allows it to meet the strict regulatory and durability requirements of diverse high-stakes industries.
| Industry | Common Parts | Key Requirement | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Dashboards, Bumpers | Impact Resistance | |
| Medical | Syringes, Vials | Sterility/Precision | |
| Electronics | Phone Cases, Connectors | Tight Tolerances |
No other process can match the breadth of application across these major economic pillars.
What Are the Main Advantages of Plastic Injection Moulding?
The primary advantages are cost-efficiency at scale, unmatched repeatability, and minimal waste. While the initial setup is an investment, the low per-unit cost makes it the most economical choice for mass production.

How Does It Save Money?
- High speed equals lower labor cost.
- One mould makes millions of parts.
- Material waste is reground and reused.
But here is the kicker: The more you make, the cheaper it gets.
Is Precision Guaranteed?
- Steel moulds are machined to microns.
- Robotic automation reduces human error.
- Parts fit together perfectly every time.
Thinking about waste? It is one of the greenest manufacturing methods available.
Key Takeaway
Plastic injection moulding offers the best return on investment for high-volume projects by combining speed, precision, and low material waste.
| Benefit | Description | Business Impact | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scalability | 1,000 to 1,000,000+ units | Growth Ready | |
| Repeatability | Identical parts | Brand Consistency | |
| Efficiency | Fast cycle times | Quick Time-to-Market |
Choosing this method positions your business for scalable growth and profitability.
How Does Design Impact Plastic Injection Moulding Costs?
The complexity of your part design directly dictates the cost of the mould and the efficiency of the plastic injection moulding process. Smart design choices can save you thousands of dollars in tooling and production fees.

Why Is Wall Thickness Critical?
- Uniform walls cool evenly.
- Thick spots cause sink marks.
- Thin walls reduce material cost.
Here is a tip: Keep your walls consistent to avoid warping.
What Are Draft Angles?
- Slight tapers on vertical walls.
- They allow the part to slide out.
- Without them, parts get stuck.
Ready for the good part? Adding draft is free during design but expensive to fix later.
Key Takeaway
Optimizing your design for manufacturing (DFM) by simplifying geometry and following standard guidelines is the most effective way to control project costs.
| Design Feature | Recommendation | Benefit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wall Thickness | Uniform (2-4mm) | Prevents Warping | |
| Draft Angle | 1-2 Degrees | Easy Ejection | |
| Ribs | 60% of Wall Thickness | Adds Strength |
A well-designed part ensures a smooth, cost-effective manufacturing journey.
Conclusion
To wrap up, the plastic injection moulding process—comprising clamping, injection, cooling, ejection, and inspection—is the backbone of modern manufacturing. Understanding these five steps ensures you can manage production expectations and maintain high quality standards. Whether you are in automotive or medical sectors, this method offers unmatched scalability. Ready to start your next project? Contact us today to discuss your design and production needs.
FAQ
Q1: What determines the cost of a plastic injection mould?The cost is primarily driven by the complexity of the part, the size of the mould, the material used (steel vs. aluminum), and the number of cavities. Complex designs requiring EDM machining or side-actions increase tooling costs significantly.
Q2: How long does the plastic injection moulding process take?The cycle time for a single part can range from a few seconds to a few minutes. This depends heavily on the wall thickness of the part (which dictates cooling time) and the type of material used.
Q3: Can you change the design after the mould is made?Modifying a hardened steel mould is difficult and expensive. It is usually possible to remove metal (to add plastic to the part), but adding metal to the mould is complex. This is why the initial design phase is critical.
Q4: What materials can be used in plastic injection moulding?There are thousands of thermoplastics available, including ABS, Polycarbonate, Polypropylene, and Nylon. Selection depends on the mechanical, thermal, and chemical requirements of the final product.
Q5: What is the difference between single-cavity and multi-cavity moulds?A single-cavity mould produces one part per cycle, which is cheaper to build but slower for volume. Multi-cavity moulds produce several parts at once, increasing upfront tooling costs but drastically reducing the unit price for mass production.