Plastic injection molding is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling mass production of precise, durable parts across industries. This article explores its mechanics, materials, and applications while addressing common challenges and innovations. Whether you’re optimizing production or exploring new technologies, this guide offers actionable insights.
1. What Is Plastic Injection Molding?\
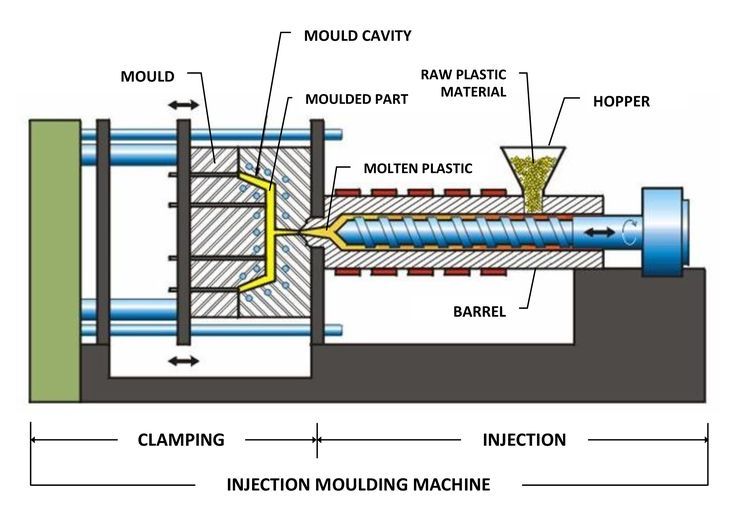
Plastic injection molding involves injecting molten plastic into a mold to create parts with high accuracy. But here’s the kicker: it’s not just about shaping plastic—it’s about repeatability at scale. The process dates back to the 19th century, evolving from rudimentary presses to today’s computer-controlled machines. Compared to blow molding or extrusion, injection molding excels in producing complex geometries like gears or medical devices.
| Method | Best For | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Injection Molding | High-precision, complex parts | High upfront tooling costs |
| Blow Molding | Hollow objects (bottles) | Limited detail |
| Extrusion | Continuous profiles (pipes) | Simple cross-sections |
A 2022 industry report shows injection molding accounts for 40% of all plastic part production. Automotive giants like Toyota rely on it for dashboard panels, while medical firms use it for sterile syringe components. What’s the real story? Without standardized molds, industries would struggle to meet global demand.
2. How Does the Plastic Injection Molding Process Work?\
The cycle starts with clamping the mold. Molten plastic is then injected under pressure, cooled, and ejected. Ready for the good part? Cycle times can be as short as 15 seconds for small parts. Machines range from 5-ton desktop units to 6,000-ton industrial giants. Hydraulic machines dominate heavy-duty applications, while electric models offer energy efficiency for precision tasks.
For example, a German automaker reduced cycle times by 20% by switching to electric machines. Temperature control systems ensure even cooling, critical for avoiding warping. This is where it gets interesting: advanced sensors now predict mold wear, slashing downtime by 30%.
3. What Materials Are Used in Plastic Injection Molding?\
Thermoplastics like ABS and polypropylene dominate due to recyclability. But wait—there’s more: engineering plastics like PEEK withstand temperatures up to 250°C, ideal for aerospace. Material choice hinges on factors like UV resistance or FDA compliance.
| Material | Strength | Cost per kg | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABS | High impact | $2.50 | Automotive trim |
| Polypropylene | Chemical-resistant | $1.80 | Food containers |
| Nylon | Wear-resistant | $3.20 | Industrial gears |
A case study from a consumer electronics firm shows switching from PVC to recycled PET cut costs by 15% without sacrificing durability.
4. What Are the Key Components of an Injection Molding Machine?\
The clamping unit holds the mold, while the injection unit melts and injects plastic. Here’s the twist: screw design impacts material mixing. A U.S. manufacturer improved part consistency by 25% using a dual-stage screw. Temperature control units (TCUs) maintain mold stability, critical for glossy finishes.
5. What Are the Different Types of Injection Molding?\
Overmolding bonds materials like rubber and plastic in one cycle. Don’t miss this: micro-molding produces parts under 1 gram with tolerances of ±0.005mm. Gas-assisted molding creates hollow structures, reducing material use by up to 40%.
6. What Are the Advantages of Plastic Injection Molding?\
High-volume output drives economies of scale. Pro tip: one mold can produce 500,000+ parts with minimal variance. A toy manufacturer cut per-unit costs by 60% after transitioning from 3D printing.
7. What Are the Common Challenges in Injection Molding?\
Sink marks occur if cooling is uneven. The solution? Simulation software like Moldflow identifies hot spots early. A case study shows a packaging company reduced scrap by 35% using real-time pressure sensors.
8. How to Design a Product for Injection Molding?\
Draft angles (1–3°) ease ejection. Key insight: uniform wall thickness prevents warping. A startup avoided $50k in redesign costs by prototyping with 3D-printed molds first.
9. What Industries Use Plastic Injection Molding?\
Medical firms leverage it for disposable tools. For instance, a Swiss company produces 10 million IV connectors annually with zero defects.
10. How to Choose the Right Plastic Material for Your Project?\
Evaluate environmental exposure. Case in point: outdoor furniture requires UV-stabilized polycarbonate.
11. What Are the Costs Involved in Injection Molding?\
Tooling can cost 10k–100k, but per-unit prices drop to cents at scale.
12. How to Maintain an Injection Molding Machine?\
Daily lubrication prevents wear. IoT-enabled predictive maintenance cuts repair costs by 50%.
13. What Are the Environmental Impacts of Injection Molding?\
Biodegradable PLA reduces landfill waste. A UK firm achieved zero waste by recycling sprues into raw material.
14. What Are the Latest Trends in Injection Molding Technology?\
AI detects defects in real-time. Hybrid molds combine metal and 3D-printed sections for complex geometries.
15. How to Start a Career in Plastic Injection Molding?\
Certifications like RJG’s Master Molder program boost employability. Apprenticeships at companies like Husky Injection Molding Systems offer hands-on training.
FAQ Section\
Q1: What is plastic injection molding?\
A manufacturing method where molten plastic is shaped in a mold to produce high-precision parts.
Q2: How does plastic injection molding work?\
Plastic pellets are melted, injected into a mold under pressure, cooled, and ejected as a solid part.
Q3: Which industries rely on injection molding?\
Automotive, medical, electronics, and consumer goods industries depend on it for mass production.
Q4: What materials are best for high-temperature applications?\
PEEK and Ultem® withstand extreme heat, making them ideal for aerospace and automotive under-hood parts.
Q5: How can defects in molded parts be minimized?\
Optimize mold design, control cooling rates, and use high-quality materials to reduce issues like warping.
Conclusion\
Plastic injection molding remains vital for efficient, scalable manufacturing. By leveraging advanced materials and AI-driven tools, businesses can cut costs and boost quality. Ready to innovate? Audit your current processes using these strategies and explore partnerships with certified mold designers.